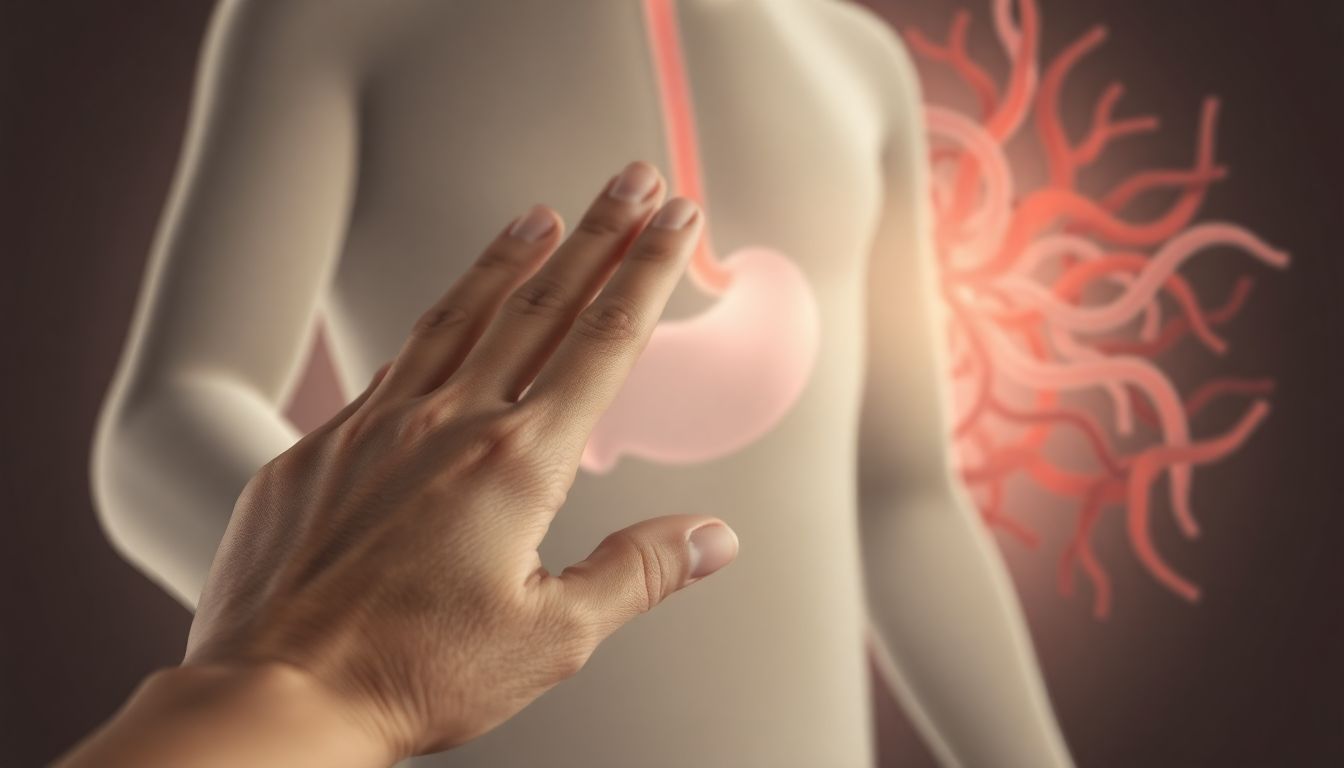
The link between stress and diabetes is often overlooked but incredibly significant. Stress can sneak up on us, affecting our bodies in ways we might not immediately notice. When stress hits, it doesn’t just mess with our heads; it can also impact our blood sugar levels, making diabetes management tougher than it needs to be. Understanding this relationship can be a game-changer for those living with diabetes.
Table of Contents
The Unseen Link Between Stress and Diabetes Connection
The hidden impact of stress on your health
Stress is more than just feeling overwhelmed at work or home. It can lead to serious health issues, especially for those with diabetes. When faced with stress, our bodies react in various ways, including changes in blood glucose levels.
Stress hormones and their effect on blood glucose levels
When we encounter stress, our bodies release hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones prepare us to react to danger but also raise blood sugar levels, making it harder to maintain stable glucose levels.
The importance of understanding this connection for better management
Recognizing how stress affects blood glucose can empower individuals with diabetes. With the right knowledge and tools, managing these stress triggers can lead to healthier blood sugar levels.
How Stress Impacts Blood Sugar Levels
The physiological response to stress and its consequences
Stress triggers a “fight or flight” response, releasing hormones that increase glucose in the bloodstream. This response creates a cycle where elevated blood sugar levels can further increase stress levels, especially for those managing diabetes.
Specific hormones involved (cortisol, adrenaline, glucagon) and their mechanisms
- Cortisol: Increases glucose production in the liver.
- Adrenaline: Raises heart rate and blood sugar levels for quick energy.
- Glucagon: Signals the liver to release stored glucose.
Case study: Examining a real-life scenario of stress-induced hyperglycemia
Consider Jake, a 30-year-old with type 2 diabetes who faces job insecurity. During stressful weeks, his blood sugar levels rise significantly, even with a consistent diet and exercise. Understanding his stress triggers helps him manage both his job stress and diabetes better.
Stress and Type 1 Diabetes
How stress exacerbates type 1 diabetes management
For those with type 1 diabetes, stress can complicate blood sugar management. An anxiety spike may lead to unplanned meals or skipped insulin doses, causing higher glucose levels.
The role of stress in triggering diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
Severe stress can trigger DKA, a dangerous condition where the body starts breaking down fat at an alarming rate. Recognizing stress as a serious factor can help prevent this.
Practical strategies for managing stress in type 1 diabetes
- Consistent monitoring: Keep an eye on blood sugar levels, especially during stressful periods.
- Open communication: Talk with healthcare providers about stress management strategies.
- Develop a support system: Build a network of friends, family, or support groups.
Stress and Type 2 Diabetes
Stress’s influence on insulin resistance and blood glucose control in type 2 diabetes
Chronic stress can worsen insulin resistance, making it harder for the body to use glucose efficiently. This can lead to more significant challenges in managing blood sugar.
The link between chronic stress and the development of type 2 diabetes
Studies show that long-term stress can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, as it can lead to unhealthy coping mechanisms like poor eating habits or lack of physical activity.
Data points showing the correlation between stress levels and diabetes complications
Research indicates that individuals with higher stress levels have a 30% greater chance of experiencing diabetes-related complications, emphasizing the need to manage stress effectively.
Managing Stress to Improve Diabetes Management
Effective stress-reduction techniques: Exercise, mindfulness, and relaxation
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can lower stress levels and improve blood sugar control.
- Mindfulness: Practices like meditation help reduce anxiety and stabilize glucose levels.
- Relaxation techniques: Simple methods like deep breathing can make a big difference.
Dietary strategies to mitigate stress-induced blood sugar fluctuations
- Balanced meals: Eating a mix of proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats can help stabilize blood sugar.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking enough water can combat stress and improve overall well-being.
Seeking professional help: Therapists, support groups, and diabetes educators
Accessing professional support can provide valuable tools for managing stress and its impact on diabetes. Consider therapy, support groups, or talking with diabetes educators.
The Role of Mental Health in Diabetes Care
The importance of mental health check-ups for people with diabetes
Regular mental health evaluations can help identify stress or anxiety that affects diabetes management, promoting overall health.
Addressing underlying mental health conditions impacting diabetes management
Conditions like depression and anxiety can complicate diabetes care. Addressing these issues can significantly improve health outcomes.
Resources and support available for managing mental health challenges
Many resources are available, including hotlines, local support groups, and online communities focused on diabetes management and mental health.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Stress and Your Diabetes
Recognizing the connection between stress and diabetes can lead to better health management. By implementing effective stress-reduction techniques and seeking support, individuals can take control of both their stress and blood sugar levels. Start by assessing your stress triggers and applying the strategies discussed in this article. Remember, maintaining a balanced mental state is just as crucial as managing your blood sugar. Take action today to improve both your mental health and diabetes management.
FAQs:
How does stress affect blood sugar levels?
Stress can cause our blood sugar levels to rise due to the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
Can stress cause insulin resistance?
Yes, chronic stress can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
How can I manage stress and improve my diabetes management?
There are several strategies you can use to manage stress and improve your diabetes management, including mindfulness-based stress reduction, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation.








Hey there,
Are you open to collaborating on editorial content right now?
We quietly work with select sites to help them grow organically, always choosing partners carefully.
You don’t need to do much — we take care of all the details.
Let me know if you’re interested!
Cheers!
Daniela
Yes, absolutely! I’m open to collaborating on editorial content right now. Let me know what you have in mind, and we can get started.”