Table of Contents
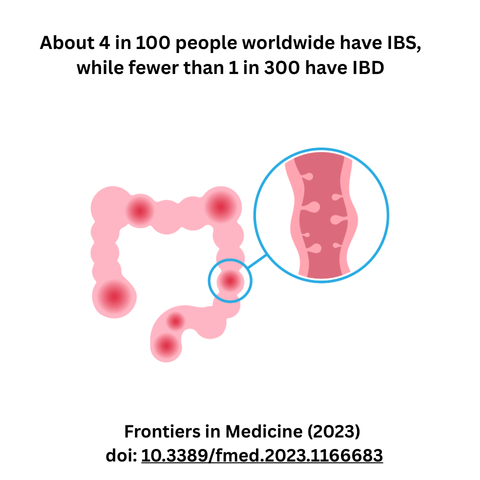
IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) and IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease). Though they sound similar and can share some overlapping symptoms, these are two very different conditions with distinct causes, complications, and treatment approaches.
IBS vs. IBD: What’s the Difference?
What Is IBS?
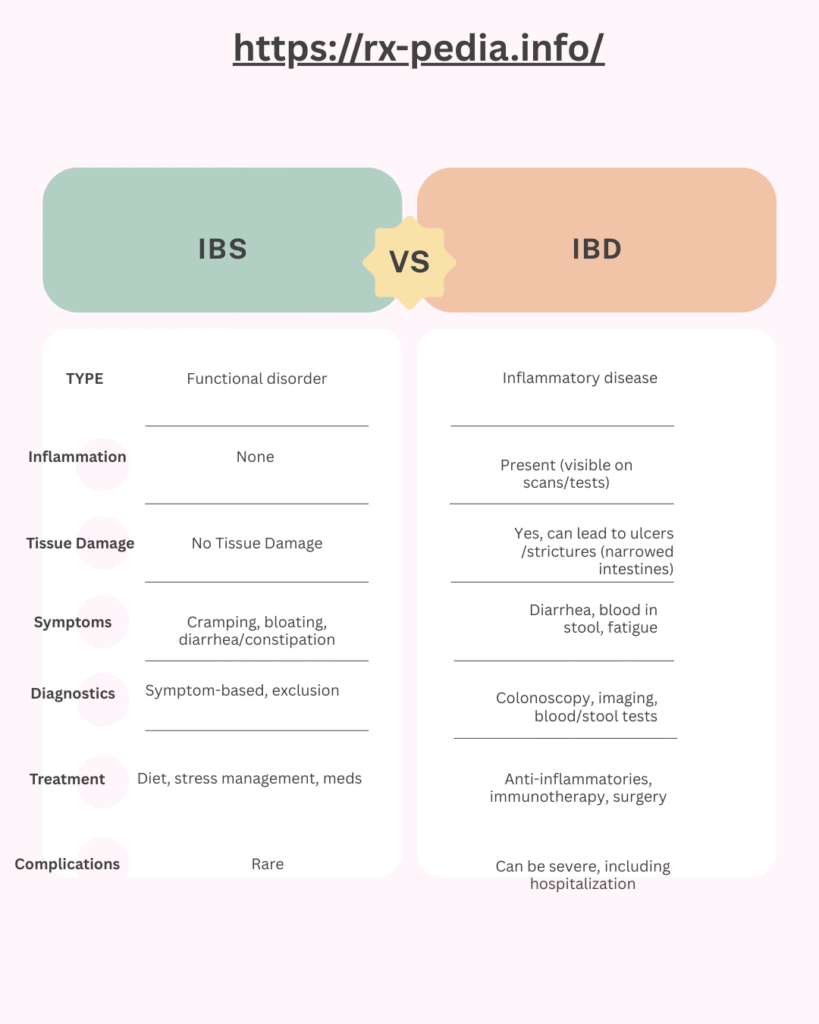
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a functional gastrointestinal disorder meaning your gut behaves abnormally but isn’t physically damaged.
Common IBS Symptoms:
- Abdominal cramping or pain
- Bloating and gas
- Diarrhea, constipation, or both
- A feeling of incomplete bowel movements
Causes and Triggers:
- Stress and anxiety
- Certain foods (like dairy, caffeine, or high-FODMAP foods)
- Hormonal changes
- Gut-brain axis dysfunction
Although IBS doesn’t cause inflammation or permanent damage to the intestines, it can significantly affect a person’s quality of life.
What Is IBD?
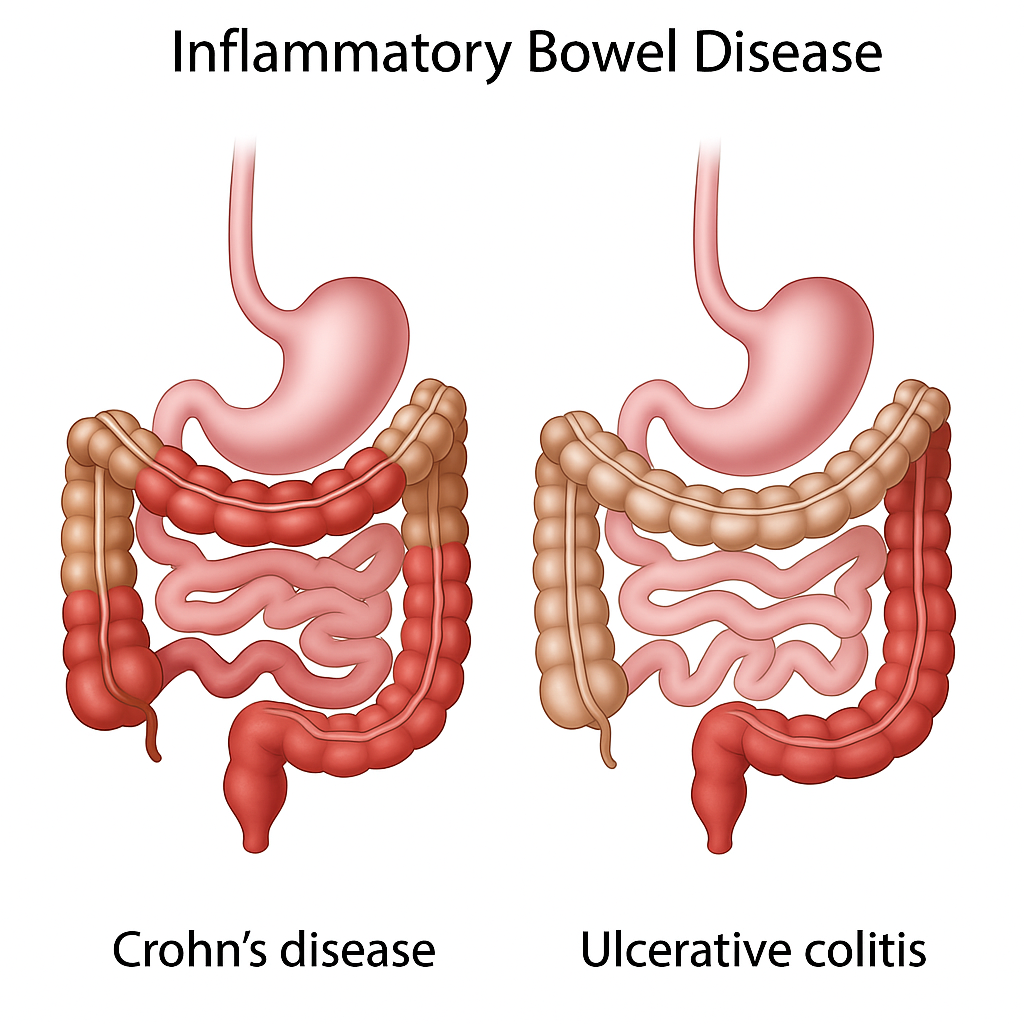
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a chronic conditions that cause inflammation in the digestive tract. The two main types are:
- Crohn’s Disease – can affect any part of the GI tract, from the mouth to the anus
- Ulcerative Colitis – typically affects only the colon and rectum
Common IBD Symptoms:
- Persistent diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Rectal bleeding or blood in stool
- Fatigue and weight loss
- Fever during flare-ups
Unlike IBS, IBD causes visible inflammation and can lead to intestinal damage, strictures, or even surgery in severe cases.
IBS vs. IBD: Key Differences
Causes & Risk Factors: IBS vs. IBD
IBS Triggers
- Food sensitivities (FODMAPs, gluten)
- Stress & anxiety (gut-brain axis plays a big role)
- Gut microbiome imbalance
IBD Causes
- Autoimmune reaction (body attacks the gut)
- Genetics (family history increases risk)
- Environmental factors (smoking worsens Crohn’s)
Research in Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2025) suggests IBD is linked to immune dysfunction, while IBS is more about gut hypersensitivity
How Are They Diagnosed?
Diagnosing IBS is primarily based on symptoms using Rome IV criteria, along with the exclusion of other conditions.
For IBD, doctors rely on:
- Colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy
- Fecal calprotectin levels
- CRP (C-reactive protein) blood test
- Imaging (CT or MRI)
These tests confirm inflammation and help differentiate between Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Can IBS Turn Into IBD?
A common myth is that IBS may evolve into IBD—but this is false.
While symptoms can overlap, IBS does not cause inflammation or lead to IBD.
A study in Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2025) reported that that misdiagnosis is common, especially since IBS symptoms can mimic mild IBD.
Treatment Options: How They Differ
IBS Treatment:
- Low-FODMAP diet((proven to reduce symptoms))
- Antispasmodics or laxatives
- Probiotics((certain strains like Bifidobacterium help))
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Stress reduction techniques
IBD Treatment:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., mesalamine)
- Immunosuppressants or biologics (e.g., adalimumab)
- Corticosteroids for flare-ups
- Surgery (in severe cases)
IBD treatment often involves long-term medication to control inflammation and prevent complications.
Living with IBS or IBD
Both conditions require lifestyle adjustments, but the severity differs. People with IBS can often manage symptoms through diet and stress control. Those with IBD may face more intensive treatment and periods of remission and flare-ups.
Regular checkups, understanding triggers, and joining support groups can improve quality of life for both conditions.
Conclusion:IBS vs. IBD: What’s the Difference?
Though IBS and IBD share some gut-related symptoms, they are fundamentally different in causes, risks, and treatments. IBS is a functional disorder without inflammation, while IBD involves serious inflammation that may require lifelong care.
If you’re experiencing persistent digestive symptoms, consult a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis can lead to better management and prevent complications—especially in the case of IBD.
FAQS :IBS vs. IBD: What’s the Difference?
Is IBS the same as IBD?
IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) is a functional disorder that affects bowel movements without causing inflammation. IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease), including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, involves chronic inflammation that can damage the digestive tract.
Can IBS turn into IBD?
No, IBS does not develop into IBD. Although symptoms like abdominal pain or diarrhea may overlap, IBS does not cause inflammation or long-term damage to the intestines like IBD does.
What are the key differences in symptoms between IBS and IBD?
IBS: Bloating, cramping, gas, diarrhea or constipation
IBD: Persistent diarrhea, blood in stool, weight loss, fatigue, fever
How is IBD diagnosed?
IBD is diagnosed through tests such as:
Colonoscopy or endoscopy
Fecal calprotectin
CRP blood test
Imaging (MRI or CT scans)
Can stress cause IBD like it does with IBS?
Stress can worsen symptoms in both IBS and IBD, but it’s not a direct cause of IBD. IBS is more sensitive to psychological triggers, while IBD is driven by immune and genetic factors.