Table of Contents
Hormones are the messengers of our body, and estrogen and progesterone are two key players in the female reproductive system. These hormones not only regulate menstrual cycles and fertility but also impact our physical and emotional well-being
What is Estrogen and Progesterone?
Estrogen: The “Growth” Hormone
Estrogen is often called the “female hormone,” but both men and women have it — just in different amounts.
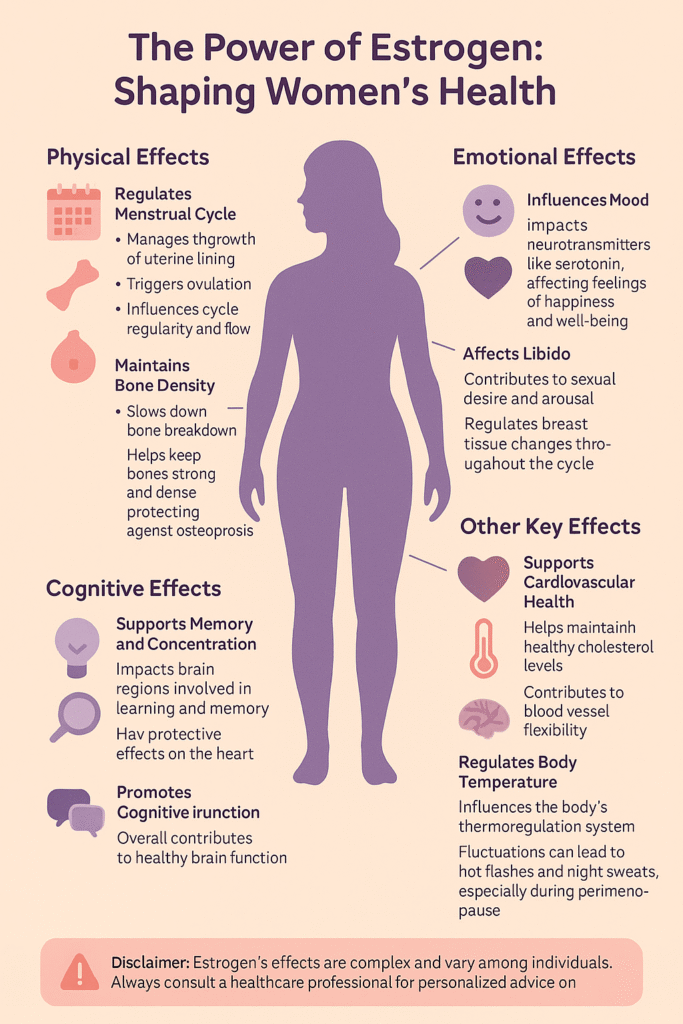
It plays a central role in regulating the menstrual cycle , supporting bone density, influencing mood , and maintaining skin elasticity.
There are three main types: estrone, estradiol, and estriol.
- Estradiol (the most potent form in premenopausal women)
- Estriol (predominant during pregnancy)
- Estrone (main estrogen post-menopause)
Estrogen is mainly produced by the ovaries , though fat cells and adrenal glands also contribute. As we age, particularly during perimenopause and menopause , estrogen levels decline, which can lead to symptoms like hot flushes, vaginal dryness, and mood changes.
Progesterone : The “Calming” and “Maintaining” Hormone
Progesterone , on the other hand, acts more like a calming, stabilizing force. It supports pregnancy, balances estrogen’s effects, and helps regulate the menstrual cycle.
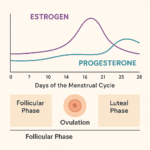
After ovulation, the corpus luteum produces progesterone to prepare the uterus for a fertilized egg. If pregnancy doesn’t occur, progesterone drops, triggering menstruation.
Its major functions include:
- Mood stabilisation
- Sleep regulation
- Supporting implantation
- Preventing excessive endometrial growth
Together, estrogen and progesterone regulate the menstrual cycle , influence libido , and affect everything from digestion to liver function .
Without enough progesterone, estrogen can become dominant — a condition known as estrogen dominance , which may lead to symptoms like heavy periods, weight gain, and anxiety.
Low progesterone levels — often seen in stress, PCOS, or perimenopause — can result in irregular periods, difficulty sleeping, anxiety, and increased PMS symptoms.
Key Differences Between Estrogen vs Progesterone
| Function | Estrogen Effect | Progesterone Effect |
| Endometrium | Builds lining | Maintains/stabilises |
| Cervical Mucus | Thin, slippery (aids sperm) | Thick, sticky (barrier) |
| Breast Tissue | Stimulates ducts | Develops milk-producing lobes |
| Mood | Energising, uplifting | Calming, sedating |
| Fluid Balance | Promotes retention | Natural diuretic |
These differences explain why estrogen dominance vs low progesterone can cause symptoms like heavy bleeding, mood swings, bloating, and acne. They also highlight why progesterone supplementation is often used alongside estrogen in hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
Estrogen vs Progesterone Effects Across the Body
Estrogen vs progesterone effects on the Brain and Neurotransmitters
Estrogen boosts dopamine, serotonin, and GABA activity , improving mood, motivation, and cognitive clarity. However, fluctuations in estrogen—especially during the menstrual cycle, postpartum, or menopause—can trigger irritability, anxiety, and depression .
Progesterone enhances GABA activity , promoting calmness and supporting sleep. Low progesterone levels are linked to insomnia and heightened anxiety , especially around your period.
Studies published in Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology (2022) show that low estrogen levels are associated with increased vulnerability to depression and anxiety, especially during perimenopause and postpartum periods.
Estrogen vs progesterone effects on the Menstrual Cycle and Fertility
Estrogen regulates the menstrual cycle by stimulating the growth of the uterine lining and plays a key role in egg maturation. After ovulation, progesterone steps in to maintain that lining in case of pregnancy.
If conception doesn’t occur, both hormone levels drop, triggering menstruation. But imbalances like high estrogen vs low progesterone can lead to irregular cycles, difficulty conceiving, and conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or fibroids .
Estrogen vs progesterone effects on the Endometrium
Estrogen promotes endometrial proliferation , while progesterone induces secretory changes and prevents hyperplasia. This dynamic is essential in preventing endometrial cancer , which is why unopposed estrogen without progesterone increases risk of endometrial cancer. .
Estrogen vs progesterone effects on the Breasts
Estrogen drives breast development and ductal growth, while progesterone stimulates lobular development and milk-producing cells. Too much estrogen without progesterone balance increases the risk of fibrocystic breast disease and possibly breast cancer .
Estrogen vs progesterone effects on Skin and Hair
Estrogen enhances collagen production, improves skin thickness, and maintains moisture levels. As estrogen declines during perimenopause , many women notice drier, thinner skin and the appearance of fine lines.
Progesterone can increase oiliness and acne, particularly in the second half of the cycle. This explains why some women experience hormonal acne around the jawline and chin before their period.
Estrogen vs progesterone effects on the Liver and Blood
The liver metabolizes estrogen. If sluggish (e.g., fatty liver), estrogen dominance can occur. Progesterone may slightly raise LDL (“bad” cholesterol), while estrogen boosts HDL (“good” cholesterol) .
Estrogen increases the production of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and clotting proteins , which is why according to the study published in Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis (2017) reported that oral contraceptives and HRT can raise the risk of blood clots.
Progesterone modulates liver detoxification enzymes and bile flow. This interaction is important when considering bioidentical hormone therapy and its effects on long-term health.
Estrogen vs progesterone effects on the Kidneys and Bladder
Estrogen influences fluid retention and electrolyte balance , while progesterone has diuretic-like effects. Hormonal shifts can affect urinary tract health, increasing the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) and incontinence .
Estrogen strengthens pelvic tissues; low levels cause “urgency” or leaks.
Estrogen vs progesterone effects on the body weight and Metabolism
Estrogen encourages fat storage in hips/thighs. A study unfold the truth that estrogen prevent the breakdown of fat in fat tissue.
Estrogen vs progesterone effects on digestion
According to the study reported that Progesterone relaxes smooth muscles, slowing digestion (constipation/bloating in PMS).
According to the study published in Menopause ,Estrogen influences gut bacteria diversity – drops in menopause may worsen IBS .
Estrogen vs progesterone effects on Fertility, Prolactin and Libido
Estrogen spikes libido near ovulation. Progesterone’s calming effect can dampen it post-ovulation. Both suppress prolactin (milk-making hormone); during pregnancy .After childbirth, progesterone and estrogen levels drop quickly , which removes the hormonal block on prolactin , allowing milk production to begin .
Special Populations: Men, Trans Individuals, and Life Stages
Estrogen vs Progesterone Effects in Transgender Health
In transgender women (male-to-female) , estrogen is typically the cornerstone of hormone therapy. It helps develop secondary female characteristics like breast growth, body fat redistribution, and softer skin.
Understanding the effects of estrogen vs progesterone in trans health can help individuals make informed choices about hormone therapy. Whether you’re considering starting hormones or simply want to understand how they work, clarity on these effects is crucial.
Despite these possibilities, most major guidelines—including those from WPATH (World Professional Association for Transgender Health) do not currently recommend routine progesterone use due to lack of robust data.
But what role does progesterone playb?And why do some clinicians include it in treatment plans?
Estrogen’s Role
- Promotes breast development
- Encourages body fat redistribution to hips and thighs
- Reduces muscle mass and facial/body hair growth
- May improve skin texture and hydration
Progesterone’s Role (in trans care)
- May enhance breast development when combined with estrogen
- Could influence mood regulation and emotional well-being
- Some theories suggest it supports nipple sensitivity and milk duct development , though this is still under study.
While estrogen is standard in feminizing hormone therapy , progesterone use is more variable. Some clinics prescribe it off-label to support certain aspects of transition, while others avoid it due to limited evidence and potential side effects.
Ultimately, the estrogen vs progesterone effects in trans health are complex and evolving. Decisions should be made in consultation with an experienced healthcare provider who understands both the science and individual needs of each person.
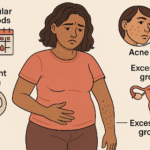
Signs of Hormonal Imbalance: Estrogen Dominance vs Progesterone Deficiency
Your body whispers (or shouts) clues:
- Estrogen Dominance: Heavy periods, fibroids, anxiety, weight gain (midsection).
- Low Progesterone: Spotting, insomnia, PMDD, recurrent miscarriages.
- Low Estrogen: Hot flashes, vaginal dryness, brain fog (common after menopause).
Track your cycle – symptoms timing reveals which hormone is off!
Can men have estrogen dominance?
Yes! Symptoms: weight gain (chest/abdomen), low libido, mood swings
Why does progesterone cause bloating?
It relaxes gut muscles, slowing digestion. Increase fibre/water!
Can progesterone cause weight gain?
Unlikely—it reduces fluid retention. Blame estrogen dominance for stubborn fat.
How do hormones affect trans men’s periods?
Testosterone therapy usually stops menstruation by suppressing ovarian hormone production.
What Happens When Progesterone Is Too Low?
Low progesterone can cause insomnia, irritability, irregular periods , and difficulty sustaining a pregnancy . Long-term deficiency may increase miscarriage risk and endometrial hyperplasia .
How Do I Know If I Have Estrogen Dominance?
Symptoms include heavy periods, PMS, bloating, fatigue, and mood swings . Confirm with a serum hormone test and consult a healthcare provider.








4 thoughts on “Estrogen vs Progesterone Effects: How These Hormones Impact Your Health”