Table of Contents
As a healthcare professional, I’ve guided countless women through the challenges of menopause and hypertension. Today, I’m sharing evidence-based insights to help you understand and manage these significant health transitions.
What Are Menopause and Hypertension?
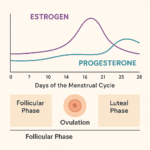
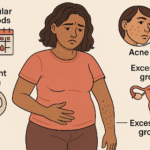
Menopause is a natural biological process marking the end of menstrual cycles, typically occurring in your 40s or 50s. It’s officially diagnosed after 12 months without a menstrual period. Meanwhile, hypertension, or high blood pressure, occurs when the force of blood against your artery walls is consistently too high.

The connection between these conditions isn’t coincidental. Research shows that post-menopausal women are at a higher risk of developing hypertension due to hormonal changes, particularly the decline in estrogen levels.
II. Causes of Menopause and Hypertension
Understanding the Root Causes
Menopause occurs when your ovaries naturally decrease their production of estrogen and progesterone. While this transition is inevitable, several factors influence its timing and severity:
- Genetics
- Lifestyle factors
- Medical treatments
- Certain health conditions
For hypertension during menopause, the causes are multifaceted:
- Hormonal changes affecting blood vessel flexibility
- Age-related arterial stiffening
- Changes in body fat distribution
- Increased salt sensitivity
- Genetic predisposition
Prevention Strategies and Risk Factors
While you can’t prevent menopause, you can manage its impact and reduce hypertension risks through:
- Regular physical activity
- Balanced nutrition
- Stress management
- Adequate sleep
- Regular health check-ups
III. Diagnosis Methods and Processes
How Are These Conditions Diagnosed?
Menopause diagnosis typically involves:
- Medical history review
- Symptom assessment
- Blood tests measuring follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and estradiol levels
- Discussion of menstrual pattern changes
For hypertension, diagnosis includes:
- Regular blood pressure measurements
- 24-hour ambulatory monitoring
- Home blood pressure monitoring
- Assessment of other cardiovascular risk factors
IV. Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Contemporary Treatment Approaches
Modern treatment options for menopausal symptoms include:
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
- Non-hormonal medications
- Lifestyle modifications
- Alternative therapies
For hypertension management:
- Antihypertensive medications
- Dietary modifications
- Regular exercise
- Stress reduction techniques
- Regular monitoring
V. Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
While menopause itself isn’t preventable, you can take steps to manage symptoms and prevent hypertension:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Follow a DASH diet
- Limit alcohol intake
- Practice regular exercise
- Manage stress effectively
- Get adequate sleep
- Regular health screenings
VI. Understanding and Managing Complications
Potential Complications
Common complications during this life phase include:
- Increased cardiovascular risk
- Bone density loss
- Weight management challenges
- Mood changes
- Sleep disturbances
- Sexual health changes
Management strategies focus on:
- Regular medical monitoring
- Preventive screenings
- Lifestyle adjustments
- Medication compliance
- Support system engagement
VII. Moving Forward: Your Action Plan
Remember these key points:
- Regular monitoring is essential
- Early intervention improves outcomes
- Lifestyle changes make a significant difference
- Professional support is valuable
- Treatment plans should be personalised
FAQs for Menopause and Hypertension
When should I start monitoring for hypertension during menopause?
Begin regular blood pressure monitoring during perimenopause, typically in your mid-40s.
Can lifestyle changes alone manage my symptoms?
While lifestyle changes are beneficial, some women may need additional medical interventions. Discuss options with your healthcare provider.
How often should I have my blood pressure checked?
During menopause, aim for at least monthly checks, or more frequently if advised by your healthcare provider.








Some really interesting points you have written.Helped me a lot, just what I was looking for : D.